Read: 04 - OOP
Java OO Tutorial
What Is an Object?
- Real-world objects share two characteristics: state and behavior.
-
Software objects are similar: they too consist of state and related behavior.
- An object stores its state in fields (variables in some programming languages) and exposes its behavior through methods (functions in some programming languages).
-
Data Encapsulation a fundamental principle of object-oriented programming that about Hiding internal state and requiring all interaction to be performed through an object’s methods.
- Software objectsbenefits:
- Modularity: The source code for an object can be decompose into a set of modules so that can be written and maintained independently of the source code for other objects.
-
Information-hiding: the details of object’s internal implementation remain hidden from the outside world.
-
Code re-use: If an object already exists (in differnet program by different developer), you can use that object in your program.
-
Pluggability and debugging ease: If a particular object turns out to be problematic, you can simply remove it from your application and plug in a different object as its replacement.
Java Classes
Declaring Classes
class MyClass {
// field, constructor, and
// method declarations
}
-
The convention to write Class Name is Capital.
- Kinds of variables:
- Member variables in a class-> are called fields.
- Variables in a method or block of code -> are called local variables.
- Variables in method declarations -> are called parameters.
- You can use a construct called varargs to pass an arbitrary number of values to a method.
To use varargs, you use (three dots, …), then a space, and the parameter name.
public Polygon polygonFrom(Point... corners) { int numberOfSides = corners.length; double squareOfSide1, lengthOfSide1; squareOfSide1 = (corners[1].x - corners[0].x) * (corners[1].x - corners[0].x) + (corners[1].y - corners[0].y) * (corners[1].y - corners[0].y); lengthOfSide1 = Math.sqrt(squareOfSide1); // more method body code follows that creates and returns a // polygon connecting the Points }1. **Pass By Value** -> when you pass Primitive arguments, such as an int or a double. 2. **Pass By Reference** -> when you pass Reference data type parameters, such as objects, as this example: ``` public void moveCircle(Circle circle, int deltaX, int deltaY) { // code to move origin of circle to x+deltaX, y+deltaY circle.setX(circle.getX() + deltaX); circle.setY(circle.getY() + deltaY);// code to assign a new reference to circle circle = new Circle(0, 0); } ```
-
Using the this Keyword -> this is a reference to the current object.
- Controlling Access to Members of a Class:
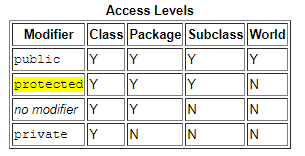
- To create an object from a class -> use the new operator and a constructor.
- The new operator returns a reference to the object that was created.
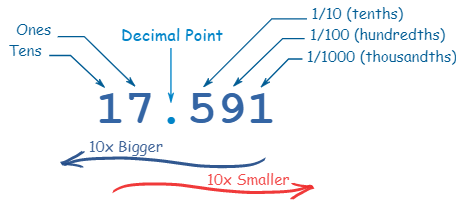
Binary, Decimal and Hexadecimal Numbers
-
The Decimal Number System OR Base 10, because it is based on the number 10, with these 10 symbols (from 0-9).
-
Binary Numbers OR Base 2 (0&1).
-
Hexadecimal Numbers 16Symbols from 0-F